What is ic Engine?

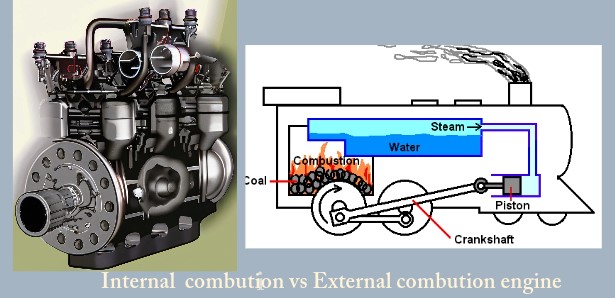
An Internal Combustion Engine (IC engine) is a mechanical device designed to convert the chemical energy stored in fuel
into mechanical energy through the process of combustion taking place within the engine, and it encompasses two primary
categories: Spark Ignition (SI) engines, prevalent in gasoline-powered vehicles, and Compression Ignition (CI) engines,
typically utilized in diesel vehicles, with both engine types serving as essential components in powering a wide range
of transportation systems and industrial machinery by harnessing the controlled explosion of fuel-air mixtures to
generate the necessary force for mechanical work.
In 1880s internal combustion engine first appeared in automobiles also in the decade the to stroke cycle engine become
practical and was manufactured in large numbers.
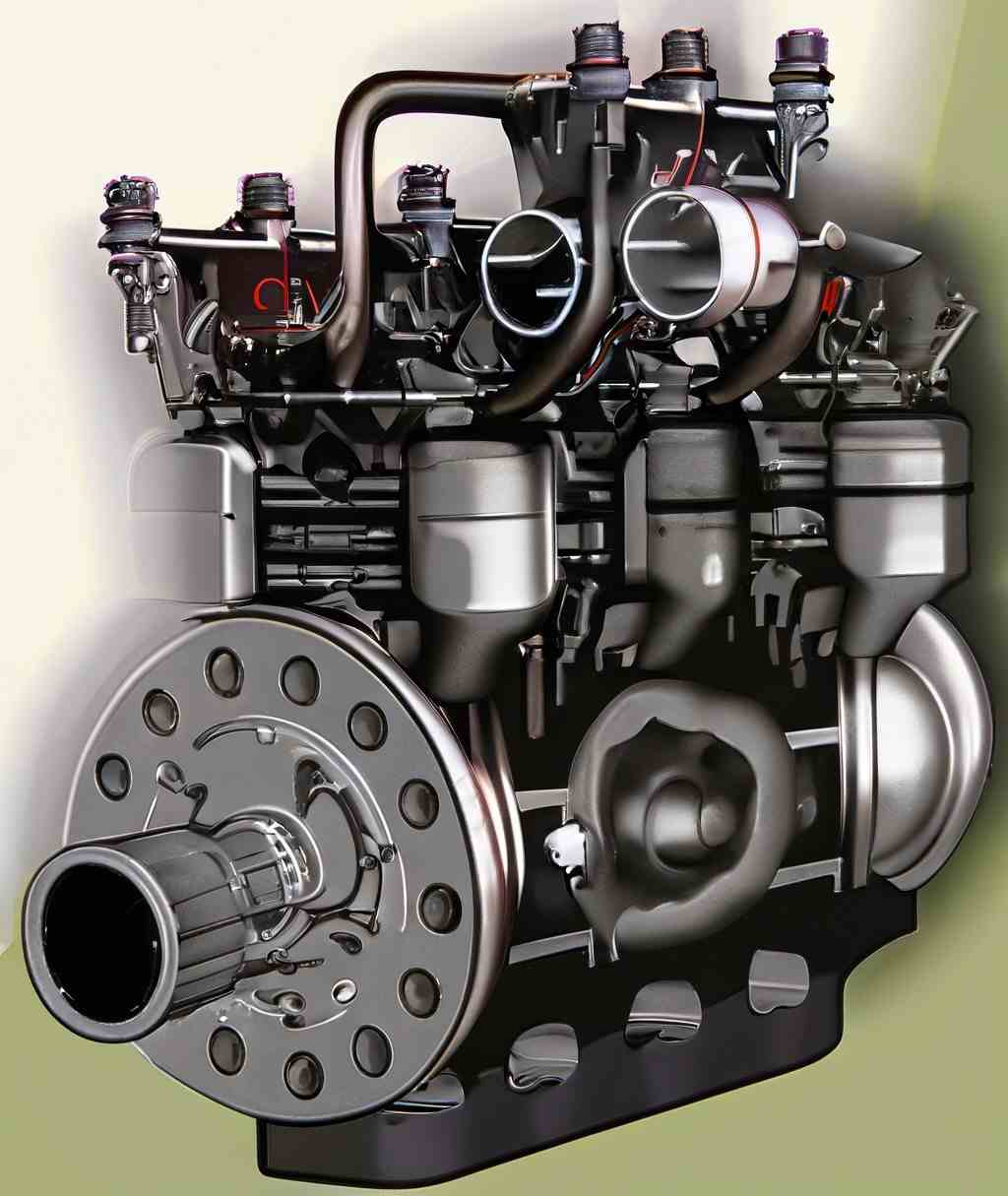
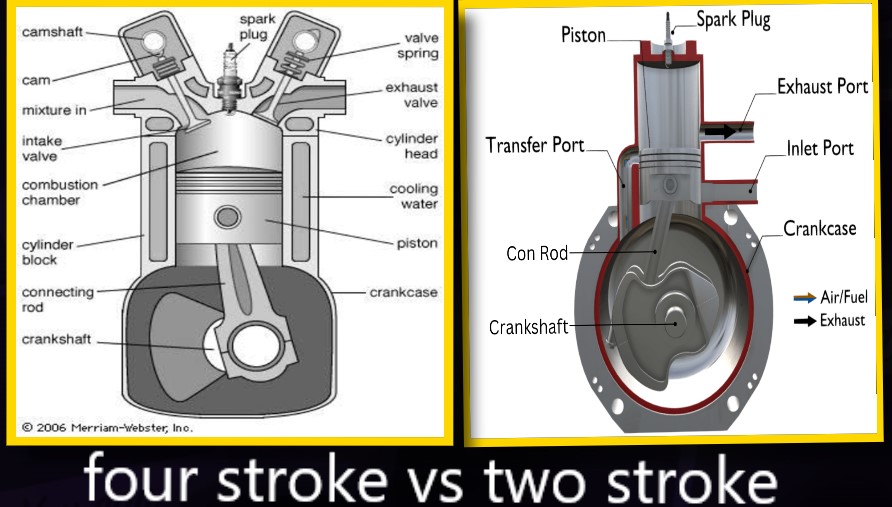
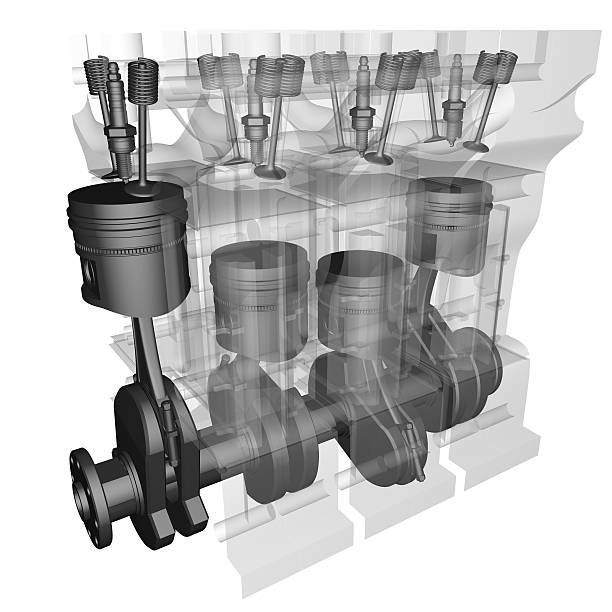
Basic components of ic engine
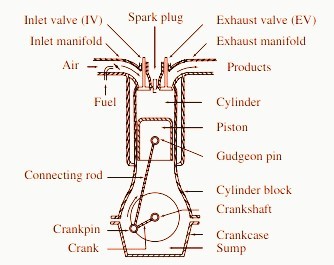
Cylinder Block : The cylinder block is the main support structure for the various components. The cylinder of a multicylinder engine are cast
as a single unit, called cylinder block. The cylinder head is mounted on the cylinder block. The cylinder head and cylinder block are provided with water
jackets in the case of water cooling or with cooling fins in the case of air cooling. Cylinder head gasket is incorporated between the cylinder block and
cylinder head. The cylinder head is held tight to the cylinder block by number
of bolts or studs. The bottom portion of the cylinder block is called crankcase.
A cover called crankcase which becomes a sump for lubricating oil is fastened
to the bottom of the crankcase. The inner surface of the cylinder block which
is machined and finished accurately to cylindrical shape is called bore or face.
Cylinder : As the name implies it is a cylindrical vessel or space in which the piston makes a reciprocating motion. The varying volume created in the
cylinder during the operation of the engine is filled with the working fluid and
subjected to different thermodynamic processes. The cylinder is supported in the cylinder block.
Piston : It is a cylindrical component fitted into the cylinder forming the
moving boundary of the combustion system. It fits perfectly (snugly) into the
cylinder providing a gas-tight space with the piston rings and the lubricant.
It forms the first link in transmitting the gas forces to the output shaft.
Combustion Chamber : The space enclosed in the upper part of the cylinder, by the cylinder head and the piston top
during the combustion process, is called the combustion chamber. The combustion of fuel and the consequent
release of thermal energy results in the building up of pressure in this part of the cylinder.
Inlet Manifold : The pipe which connects the intake system to the inlet
valve of the engine and through which air or air-fuel mixture is drawn into
the cylinder is called the inlet manifold.
Exhaust Manifold : The pipe which connects the exhaust system to the
exhaust valve of the engine and through which the products of combustion escape into the atmosphere is called the exhaust manifold.
Inlet and Exhaust Valves : Valves are commonly mushroom shaped poppet type. They are provided either on the cylinder head or on the side of the
cylinder for regulating the charge coming into the cylinder (inlet valve) and for discharging the products of combustion (exhaust valve) from the cylinder.
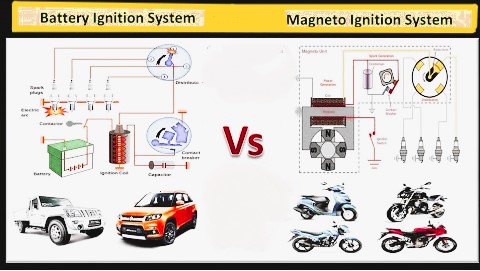
Spark Plug : is a component to initiate the combustion process in Spark Ignition (SI) engines and is usually located
on the cylinder head.
Connecting Rod : It interconnects the piston and the crankshaft and transmits the gas forces from the piston to the
crankshaft. The two ends of the connecting rod are called as small end and the big end Small end is connected to the piston by gudgeon pin and the big end is connected to the
crankshaft by crankpin.
Crankshaft : It converts the reciprocating motion of the piston into useful
rotary motion of the output shaft. In the crankshaft of a single cylinder
engine there are a pair of crank arms and balance weights. The balance
weights are provided for static and dynamic balancing of the rotating system.
The crankshaft is enclosed in a crankcase.
Piston Rings : Piston rings, fitted into the slots around the piston, provide
a tight seal between the piston and the cylinder wall thus preventing leakage
of combustion gases.
Gudgeon Pin : It links the small end of the connecting rod and the piston.
Camshaft : The camshaft (not shown in the figure) and its associated parts
control the opening and closing of the two valves. The associated parts are
push rods, rocker arms, valve springs and tappets. This shaft also provides
the drive to the ignition system. The camshaft is driven by the crankshaft through timing gears.
Cams : These are made as integral parts of the camshaft and are so designed to open the valves at the correct timing
and to keep them open for the necessary duration.
Fly Wheel : The net torque imparted to the crankshaft during one complete cycle of operation of the engine fluctuates causing a change in the angular
velocity of the shaft. In order to achieve a uniform torque an inertia mass in the form of a wheel is attached to the output shaft and this wheel is called the flywheel.
Classification of ic engine
internal combustion engine in classified as a given below:
According to cycle of operation:
- Two stroke cycle engine
- four stroke cycle engine
According to cycle of combustion:
- Otto cycle engine (combustion at constant volume)
- diesel cycle engine( combustion at constant pressure)
- dual-combustion and semi-diesel cycle( combination engine partly constant volume and partly constant pressure)
According to the arrangement of cycle:
- single cylindrical cycle engine
- in-line straight engine
According to arrangement of cylinder:
- Single cylinder engine
- Cylinder engine
- Inline or straight engine
- V engines
- Opposite cylinder engine
- W-engine
- opposite piston engine
- radial engines
According to the their uses:
- Stationery engine
- portable engine
- Marine engine
- automobile engine
- aero engine etc
According to the speed of the engine:
- low speed engine
- high speed engine
According to the method of ignition:
- Spark ignition engine
- compression ignition engine
According to method of calling the cylinder:
- air cooled engine
- water cooled engine
According to the valve arrangement:
- overhead valve engine
- L head type engine
- T-Head type engine
- F-head type engine
According to the method of governing :
- quality governed engine
- hit and miss governed engine
- quantity governed engine
According to the number of cylinder:
- single cylinder engine
- multi cylinder engine
According to air intake process:
- Normally aspiranted, no Intake air pressure boost system
- Supercharged, intake air pressure increased with the compressor driven off the engine crankshaft
- turbocharged, intake air pressure increased with the turbine compressor driven by the engine exhaust gasses.
- Crankcase compressed, two stroke cycle engine which use the crankcase the intake air compressor limited developed work
has also been done on the design and construction of four stroke cycle engine with crankcase compression
According to the fuel employed:
- Oil engines
- Petrol engines
- Gas engines
- Kerosene engines
- LPG engine
- Alcohol ethyl, ethyl engines
- dual fuel engine (90% gasoline and 10% alcohol )
Method of fuel input for SI engine:
- carburated
- Multi point port fuel injection one or more injectors at each cylinder Intake.
- throttle body fuel injection injectors of stream in intake manifold.
Application of IC engine:
the Ic engine are generally used for:
- Road vehicle (as. scooter, motorcycle, buses etc)
- Aircraft,
- Locomotive
- Construction in a civil engineer equipment such as bulldozer scraper power soils etc
- Pumping sets
- Cinemas
- Hospital
Several industry application application of various industry separately or listen below:
small two-stroke petrol engine:
- simplicity and the low cost of primary mobile are primary consideration.
- The 50 cc engine developed maximum break power of 1.5 kilowatt 5000 RPM and is used in mopeds.
- 100cc engine developing maximum break power of about 3 kilowatt 5000 RPM is used in scooter.
- the 150 cc engine development maximum break power of about 5 kilowatt 5000 RPM
- 250 cc engine development break power of about 4500 RPM in general used in motorcycle
The engine also find application in very small scooter electric generating set pumping sets etc
small four-stroke petrol engine:
- these engines are primary used in automobiles
- these are used in pumping set and mobile electric generating set
Four stroke diesel engine
diesel engine is employed for following :
- pumping set
- construction machinery
- Air compression and drilling jigs
- tractors
- Jeep car and taxi.
-
- mobile and stationery electric generating plant
- diesel electric locomotive
- boat and ships
Two Stroke Diesel Engine
These engine having very high power are usually employed for ships propulsions
Radial piston engine in small aircraft Propulsion:
- Radial piston four stroke Petrol engine having power range from 300 kilowatt to 4000 KW have been used in small aircraft
- In modern large aircraft instead of these engine gas turbine plant as turboProp engine or turbojet engine and gas
turbine engine are used.